The US market from the perspective of California and Texas
After Belgium and France, we are visiting the US battery market together with Arenko. The American market is a combination of 9 independent grids, CAISO (California Independent System Operator) and ERCOT (Electric Reliability Council of Texas)with a combined 8 GWs of installed battery capacity being the largest. However, the two exhibit differing market fundamentals, philosophies and alignment principles. California, for one, endorses interconnectivity and is integrated with neighboring regions as well as WEIM (Western Energy Imbalance Market), which allows them to manage supply and demand in real-time and venture into day-ahead trading territory. They are also active in the capacity market, using a construct referred to as resource adequacy (RA), which promotes long-duration assets with participation in wholesales and an obligation to discharge over an extended period of time.
Texas, on the other hand, is an energy-only marketplace without interconnectors or capacity markets. Instead, they use a method called scarcity pricing, which caps the price at USD 5,000/MWh. As of spring 2023, the state has no concrete plans to introduce a capacity market in the near future. Despite the striking disparities in the Californian and Texan market designs, batteries are addressing the unique challenges of both.
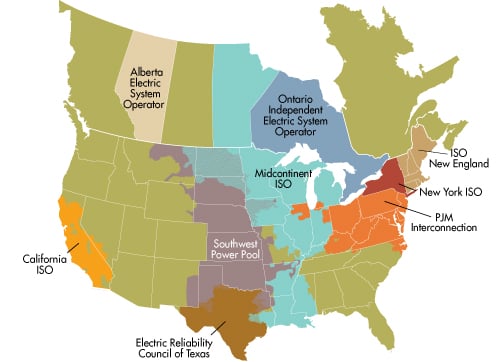
The 9 independent system operators in the US
Source: CAISO
Current growth drivers
Grid challenges
Grid problems in the United States become evident during extreme weather events and thermal outages. When Storm Eliot hit in winter 2022, there was a considerably higher availability of wind and battery capacity than during Storm Uri. When Uri happened, prices soared to unprecedented levels (from $1,200/MWh to $9,000/MWh), triggering the aforementioned price cap, which in turn resulted in a comparatively lower price hike during Elliot ($3,700/MWh). The increase in battery capacity enabled ERCOT to keep the lights on throughout Elliot's destruction. Meanwhile, in California, battery systems offer a reliable solution to CAISO's duck curve and curtailment issues.
To illustrate these problems, solar generation in California rises steadily throughout the day and tails off as evening time approaches even though demand remains consistent or increases depending on weather activity and need for air conditioning. At the same time, California has a practice of curtailing renewable resources because of congestion in the transmission system. Batteries, therefore, charge during solar hours and discharge during net load peaks.
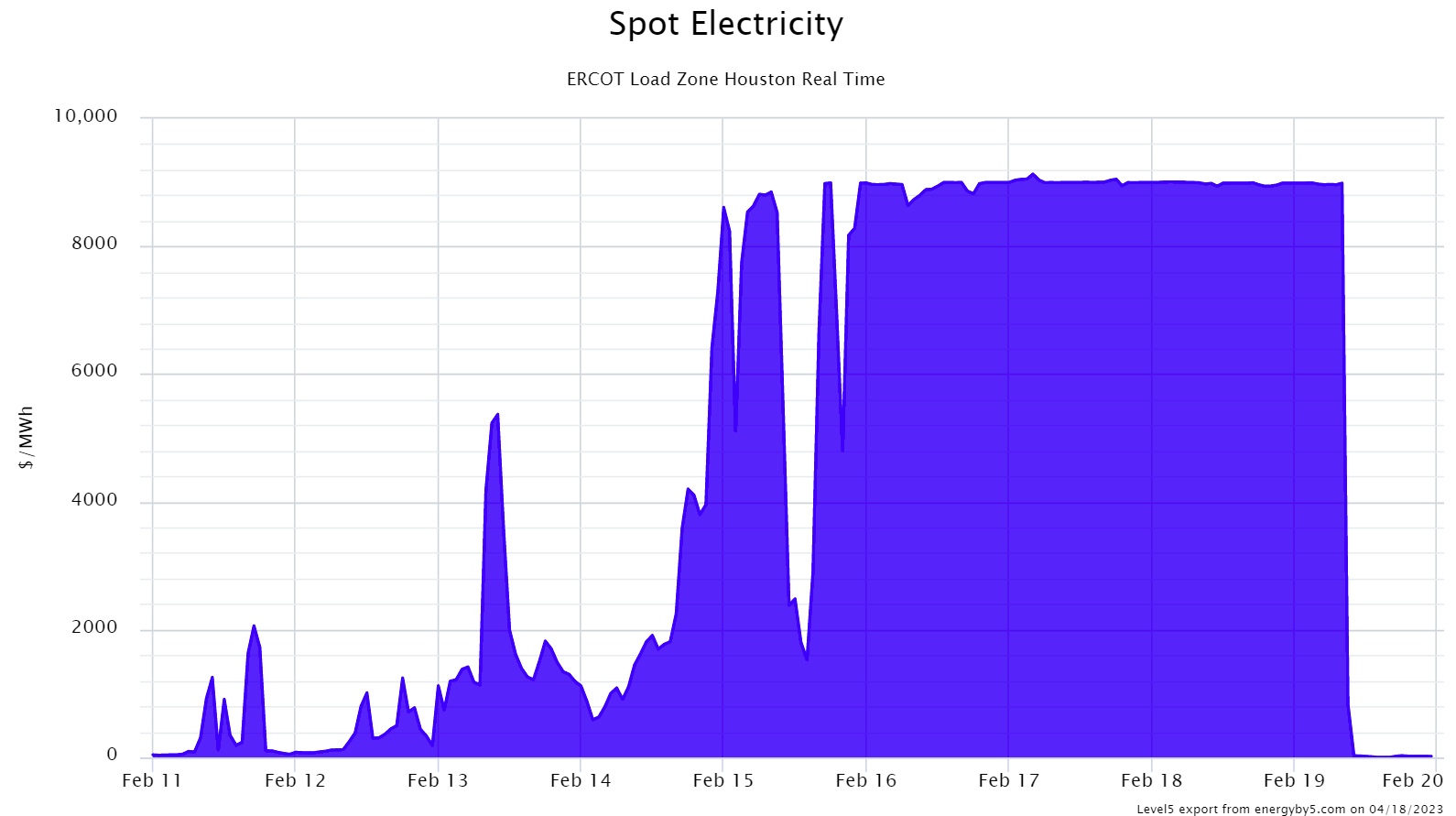
Source: energyby5
Investments
The American systems differ from the UK and mainland Europe in that they employ a nodal market construct with locational marginal prices (LMP), which are refreshed every 5 minutes in real time and hourly in day-ahead. Within the frame of this much more granular system, locational aspects of grid installations must be considered as they can impact revenue. In California, all forms of battery market participation are available and can be stacked. These include the capacity market, resource adequacy, energy arbitrage, operating reserves and regulation. Texas supports the majority of them, bar the capacity market. CAISO also shows that co-located batteries are more profitable than standalone assets because they benefit from their renewable co-installations, while independent batteries suffer from high charging prices. In ERCOT, most batteries make money through ancillary services, but trend forecasts point towards more volatility and greater arbitrage opportunities due to the expanding penetration of solar and wind. As the Texan market is less saturated, many new entrants prefer asset building in this location over California.
Market predictions
The IRA (Inflation Reduction Act) is expected to advance BESS (battery energy storage system) deployments as standalone assets now qualify for investment tax credit. The following factors are currently the main accelerators of battery markets and BESS development in the United States:
- favorable electricity market structure
- high renewable energy penetration
- strong revenue streams
- extensive grid modernization efforts
US battery storage capacity by 2025
The US Energy Information Administration (EIA) outlines significant growth in the battery capacity that is planned to be installed across the country, most prominently in Texas and California, by 2025. Due to the indisputable benefits and declining cost of the technology, batteries are becoming increasingly attractive for investments and government funding, thus supporting the effort to meet important climate goals.
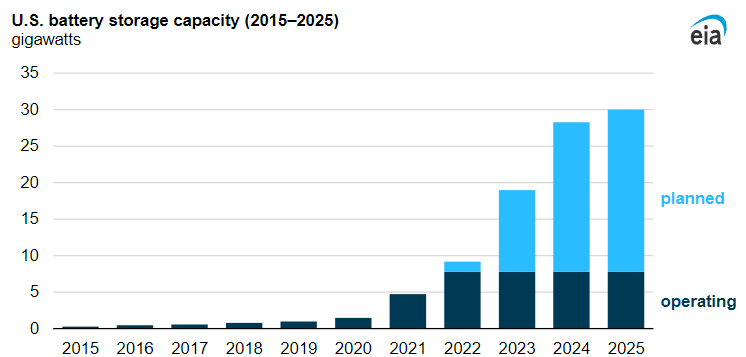
Source: EIA
Interested in more international battery markets?
Read about Belgium and France and how these assets are optimally traded. Also, make sure to follow us on LinkedIn to stay on top of the latest developments.
