Inside Germany's storage future
A 2023 study commissioned by enspired, BayWa r.e., ECO STOR, Fluence and Kyon Energy Solutions and conducted by Frontier Economics highlights the vast economic potential of grid-scale battery storage in Germany. With the energy-transition-endorsing technology set to grow exponentially until 2030, industry representatives are appealing to policymakers for a modification of the regulations governing storage integration. The rise of storage capacity is expected to be entirely market-driven, meaning without any subsidies from the state.
Why battery storage deserves regulatory acceptance
As the energy transition progresses toward a carbon-neutral future, fossil-based energy sources are gradually being phased out or replaced by renewable alternatives. This fundamentally transformed Germany’s power system – by the end of 2023, the share of renewable energies in the gross electricity consumption had risen to 56%, up from 46% in 2022 and from 6.3% back in 2000. Until 2045, planned decarbonization efforts will become increasingly difficult due to the intensifying demand for electrification as well as the unavailability of facilities previously used for this purpose.
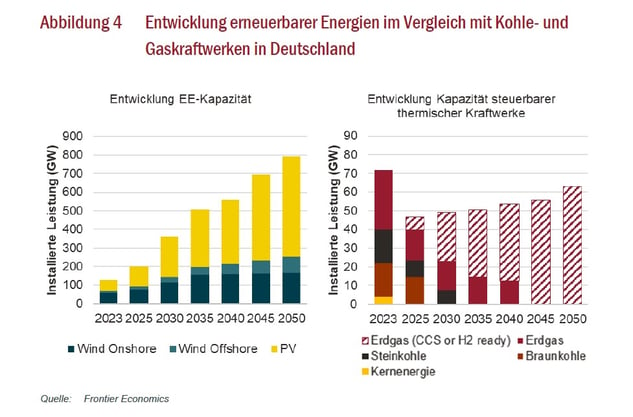
The graph shows the development of renewable sources compared to coal and gas plants in GWs installed until 2050. The chart on the right differentiates between (from top to bottom) natural gas (CCS or H2 ready), coal, nuclear energy, natural gas and lignite.
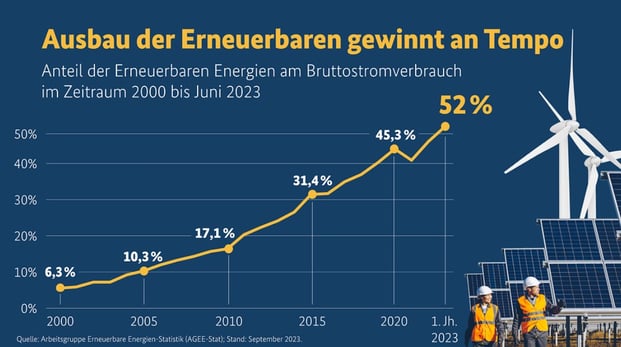
The graph shows the development of renewable energies between the years 2000 and the first half of 2023.
Grid-scale battery storage is one of the most promising technologies for the advancement of the energy transition. Electrical energy is stored during periods of low demand or high supply and released during periods of high demand or low supply. Unlike residential or EV batteries, grid-scale storage is conceptualized specifically for market participation as it offers higher power and capacity levels. Therefore, its flexibility can be capitalized across relevant markets, ultimately engendering a reduction in price volatility and price risk for market participants and lower electricity costs for consumers. Between 2030 and 2050, calculations reveal savings of an average 1€/MWh. An important driver of this development is the significant decline in manufacturing costs for battery storage technology in recent and expected upcoming years.
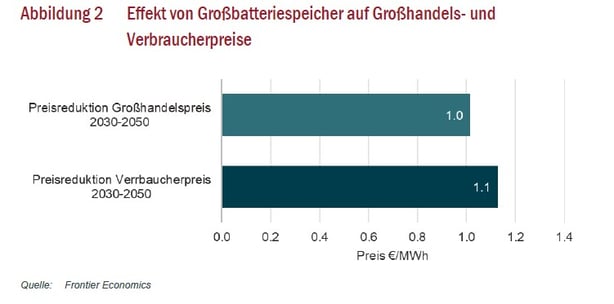
The graph shows the effect of grid-scale battery storage on wholesale (top) and consumer (bottom) prices between 2030 and 2050 in €/MWh.
The Bloomberg New Energy Finance (BNEF) research institute is anticipating substantial annual growth in battery storage capacities worldwide. Comparable trends are expected in Germany. Through the market simulation attached to this study, contributors came to similar results as independent prognoses by Frauenhofer ISE, the Ten-Year-Network-Development Plan (TYNDP) and the 2023 Netzentwicklungsplan (NEP – ‘Net Development Plan’). For Germany, forecasts estimate a climb to 15 GW/57 GWh until 2030, to 24 GW/94 GWh until 2040 and to 61 GW/271 GWh until 2050. Battery units with a storage duration of 4 hours are especially interesting for filling the market demand. It should be noted that since the simulation considers only the day-ahead market, additional battery revenues – financed through the intraday and ancillary service markets – can be assumed.
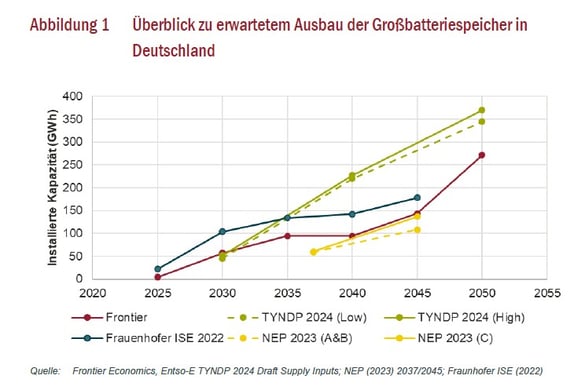
The graph shows current projections for the grid-scale battery storage expansion in Germany in GWhs installed until 2050.
Grid-scale battery storage brings €12bn in economic welfare gain
The market simulation shows that even though grid-scale batteries cause an overall increase in electricity demand due to efficiency losses during the charging process, they simultaneously bring in an economic value of 12 € billion with their load-shifting properties through the day-ahead wholesale market alone. These results come to light in comparison with an event scenario in which Germany experiences a stagnation of new market-based battery installations. In this scenario, the market must replace battery capacities with other forms of generation. On a related note, grid-scale battery storage is set to help save an estimated 6.2 and 7.9 million tons of CO2 in the years 2030 and 2040, respectively.
Storage flexibility strengthens renewable integration and compensates intraday forecast errors
Next to the wholesale market, battery storage is also becoming increasingly important for the flexibilization of the power system. The market simulation performed within the scope of this study projects an increase of installed wind and solar capacity to 360 GW by 2030, to 562 GW by 2040 and to 792 GW by 2050. The rapidly growing integration of renewable energies is accompanied by an enormous flexibility demand that can balance out the associated fluctuations in the grid. As coal and gas plants are simultaneously losing more and more ground in the energy world, grid-scale battery storage is gaining traction as a long-term answer to the flexibility question. Batteries have very agile, high-speed response systems that improve liquidity in the intraday market. This allows market participants to strengthen their position by addressing sudden changes in supply and demand with enhanced reactivity and greater efficiency. Intraday liquidity plays a crucial role in risk management, most of all in volatile markets. Short-term adaptability yields considerable benefits not just for the protection against unforeseeable market conditions but also for the minimization of price risks. Beyond this, the intraday market facilitates the trading of renewable forecast errors, eliminating the need for expensive compensatory control energy.
Grid-scale battery storage for ancillary services
Batteries are ideally suited for various grid and ancillary services, including but not limited to frequency regulation, voltage control, black start capability, congestion management and instantaneous reserve. With an adequate regulatory framework in place, batteries could be leveraged much more pointedly to accelerate the shift to renewables, all the while lowering the overall cost of grid services.
Grid-scale battery storage eases pressure to invest in gas-fired power plants
Lastly, the study emphasizes the pressure to invest in gas plants that would arise in a scenario where the battery storage network does not mature as projected. 26 GW of planned gas capacity is not enough to cover the demand, and an additional 9 GW would be required to keep up. In the projected battery storage scenario, the new gas plants would serve as more of a backup device that can be activated in times when renewables are struggling to meet the demand.
This raises the question of how the expansion of battery storage is progressing in Germany. Several domestic and foreign battery project developers are already in the process of building and installing storage facilities for a widespread feed-in into the German power system, and new plans are sanctioned on a regular basis.
Refined regulatory framework needed to exploit the full potential of battery storage in Germany
On EU level, the importance of battery storage has been recognized, prompting storage-friendly measures in many countries. In Germany, a storage strategy is currently still in development. This is the right direction, but to be able to leverage battery storage technology in a manner that will fundamentally shape the energy transition, it is of the essence to have transparent legal and regulatory guidelines in place that will give project owners and asset operators planning security and access to relevant markets. For this, a distinct vision of how to effectively utilize battery storage to cater to system needs is as important as continued market development. Cementing battery storage as an independent pillar in the energy landscape would send a strong signal and make future legislation fit for purpose.
For further insights, read the complete study.
